
The purpose of this study is to create a cutaneous lymphoma tissue repository. This is a highly significant first step in collecting specimens for future analysis to understand the underlying drivers of disease.
#CUTANEOUS TCEL LYMPHOMA TRIAL#
The purpose of this trial is to evaluate the antitumor activity of Pembrolizumab in patients with advanced mycosis fungoides (MF) as initial systemic therapy. Trial Using Keytruda as Initial Therapy in the Treatment of Advanced Mycosis Fungoides.The activated drug may kill cancer cells. Photodynamic therapy uses a drug, such as aminolevulinic acid hydrochloride, that becomes active when it is exposed to light. This pilot phase II trial studies how well photodynamic therapy works in treating patients with mycosis fungoides that does not respond to treatment. Photodynamic Therapy in Treating Patients With Refractory Mycosis Fungoides.Drugs used in chemotherapy work in different ways to stop the growth of cancer cells, either by killing the cells or by stopping them from dividing This phase II trial studies how well combination chemotherapy and pralatrexate works in treating patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). Scottsdale/Phoenix, AZ Jacksonville, FL Rochester, MN Combination Chemotherapy and Pralatrexate as First-Line Therapy in Treating Patients With Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma.To investigate the efficacy of autologous EBV-specific T-cells for the treatment of patients with aggressive EBV positive extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma Cellular Immunotherapy Treatment Antigen-Directed for EBV Lymphoma.The purpose of this study is to learn about the effects of a research medicine called AFM13 and to see how well AFM13 is tolerated. Phase II Study to Assess AFM13 in Patients With R/R CD30-positive T-cell Lymphoma or Transformed Mycosis Fungoides.
#CUTANEOUS TCEL LYMPHOMA SKIN#
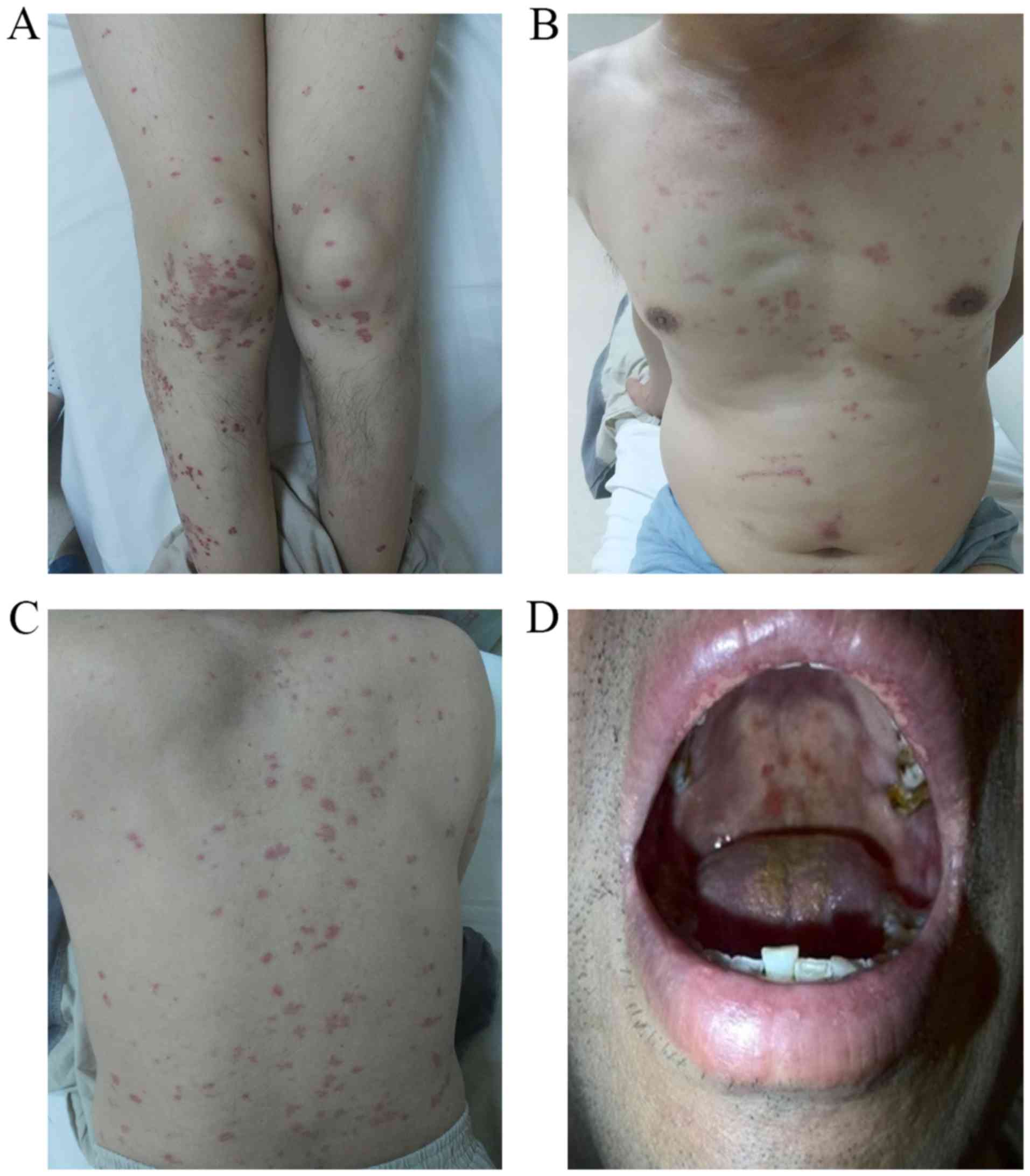
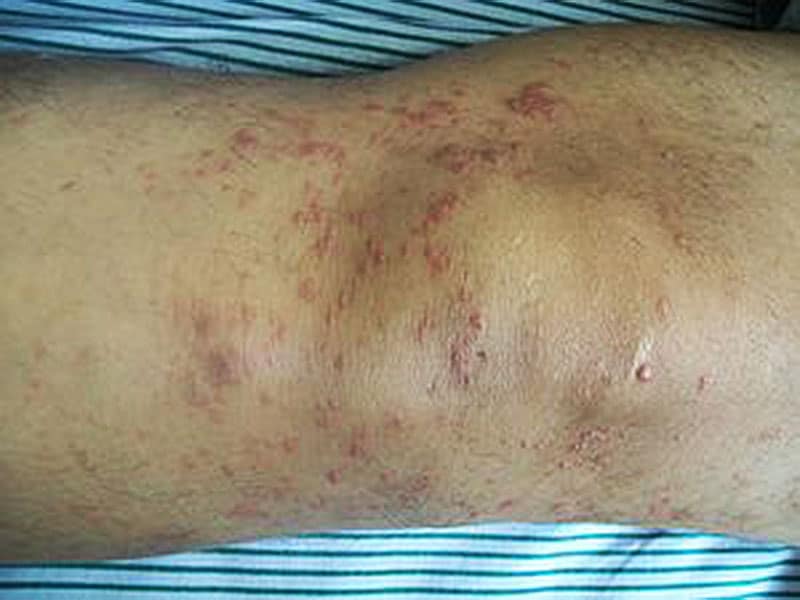
Systemic or nodal B-cell lymphomas can secondarily involve the skin, and when a skin biopsy shows B-cell lymphoma it is very important to make sure that the lymphoma is truly coming from the skin and not from a systemic lymphoma that has spread to the skin.įor a more in depth overview, watch Cutaneous Lymphoma 101. Primary cutaneous follicle center and primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphomas are the most common forms of CBCL, and are slow growing or indolent types that respond well to mild treatments. There are 3 main types of CBCL primary cutaneous follicle center (“follicular”) lymphoma, primary cutaneous marginal zone (“MALT”) lymphoma, and primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell (DLBCL, “leg type”) lymphoma. CUTANEOUS B-CELL LYMPHOMAS (CBCL)Ĭutaneous B-cell lymphomas (CBCL) make up about 20-25% of all cutaneous lymphomas, and are cancers that develop from skin-based B-cells. chronic, slowly growing) lymphomas – treatable, but not curable, and usually not life-threatening. Most people with CTCL have indolent (i.e. Only a minority of people with CTCL develop advanced disease, with tumor formation, ulceration, involvement of lymph nodes, blood, and internal organs. CTCL often mimics eczema, psoriasis, or other chronic dermatitis, and because of this it’s common that the diagnosis of CTCL is delayed, sometimes by years or decades. Itching is common, with more than 80% of people with CTCL reporting they have itch. Upcoming Events for Medical ProfessionalsĬutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) is the most common type of cutaneous lymphoma, and typically presents with red, scaly patches or plaques on the skin.Primary Cutaneous Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (PCALCL).Primary Cutaneous B-Cell Lymphoma (CBCL).Folliculotropic Mycosis Fungoides (FMF).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
